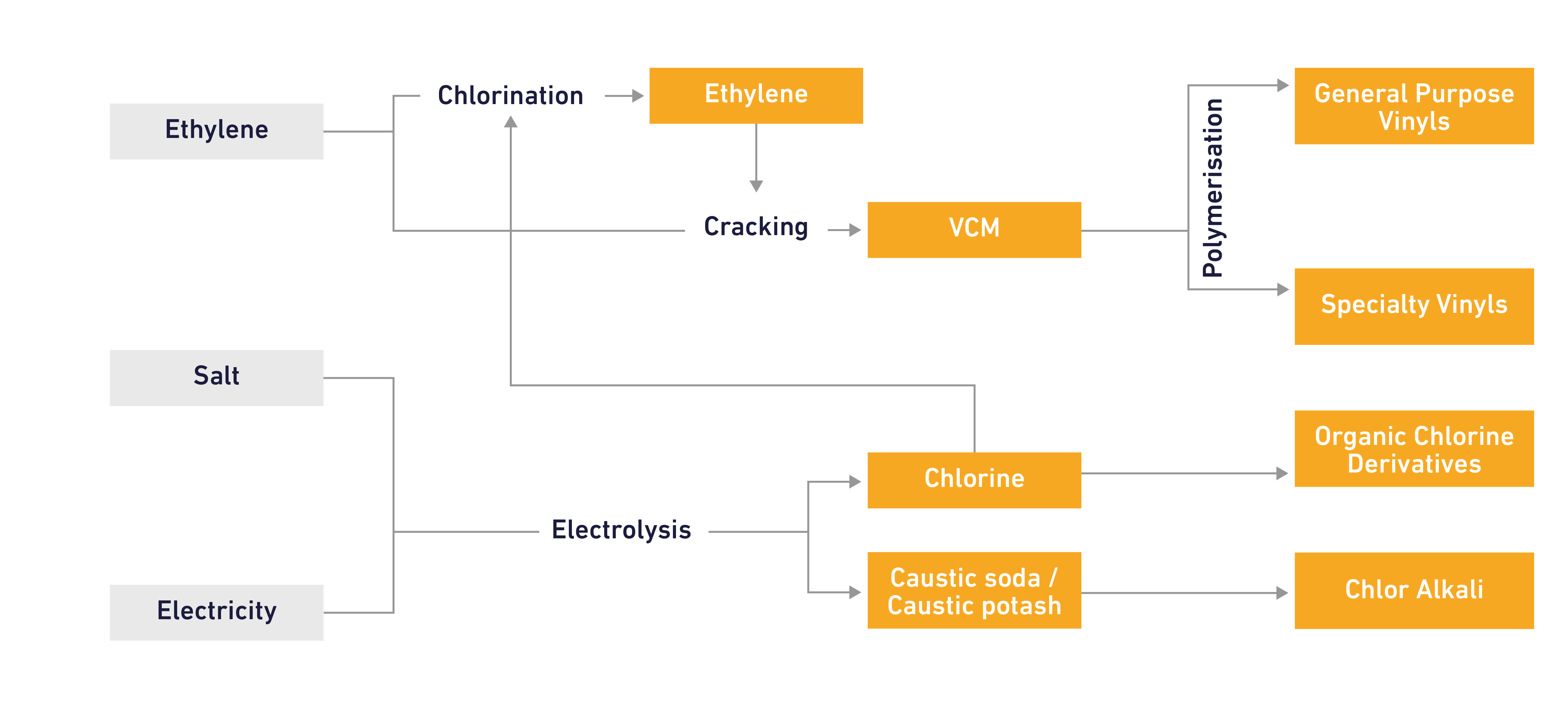
Caustic soda is produced in cellrooms by passing a powerful electric current through a brine solution (salt dissolved in water). The resultant chemical reaction produces chlorine and caustic soda, or chlorine and caustic potash, in fixed ratios, along with a small amount of hydrogen that can be used as fuel or for other chemical applications.
Caustic soda is a widely used industrial chemical, including in pulp and paper, detergents, packaging, agriculture, environmental protection, water treatment, foodstuffs, health, textiles and in the chemical, construction and car industries.
Caustic soda is produced in liquid and solid forms. Liquid caustic soda is a strong base used as a chemical reagent, a pH-regulator, an ion exchange resin regenerating agent, catalyst and etching and cleaning agent. Solid caustic soda has similar properties but is manufactured by evaporation of water from liquid caustic soda, followed by solidification into micro pearls.